Filter By
Closed Opportunities
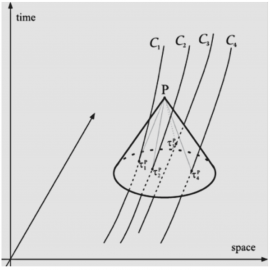
Feasibility study of a space-based relativistic PNT system
All GNSS in operation at present are based on Newtonian physics and rely on global reference frames fixed to Earth. Relativistic effects are treated as deviations that need to be corrected for. Precision and stability over time of the reference frames is provided via ground stations and they are limited by the Earth’s dynamics (e.g. variations of the Earth’s rotation rate, plate tectonics,…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
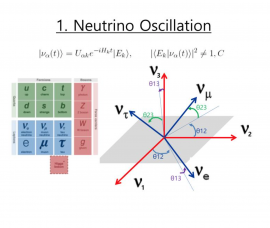
PNT using Neutrino Particles
This proposed activity represents an innovative concept to realise Positioning, Navigation and Timing using neutrino particles. At present, standard navigation approaches – including satellite navigation – rely on direct line-of-sight RF and optical communications. Neutrinos move at around the speed of light, have no electric charge and are low mass, thus showing very low interaction with…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
Quantum-based sensing for PNT
The exploitation of quantum physics has already enabled revolutionary technical applications and industries of enormous economic scale. The semiconductor industry alone is currently a €500 billion market, giving rise to industries on an even larger scale (smartphones, computing, software, etc.).
Quantum physics is now again set to radically change several industries, including…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
Trusted Radionavigation via Two-Way Ranging
Wireless positioning systems based on passive ranging, as used in GNSS today, are very attractive and represent the most pragmatic and cost-beneficial solution for worldwide positioning in benign, secured environments; however, this may no longer be a one-size-fits-all solution for modern radionavigation usage as the need for complementary solutions offering adaptability, reliability and trust is…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
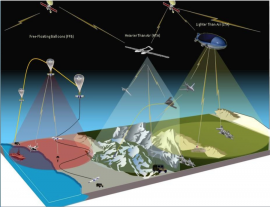
High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellites for PNT
High-Altitude Pseudo-Satellites (HAPS) are airships “quasi-”stationed at a height of 20-30 km, in an altitude range where atmospheric winds are milder. HAPS are normally solar powered, unmanned, large, helium filled and semi-rigid; they can be operational for several years.
HAPS have been studied in the telecom domain (ESA GSP HAPPIEST study), where they were briefly considered…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
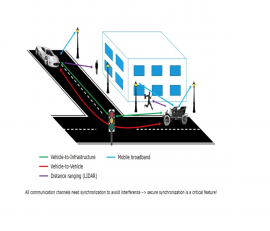
Resilient, Trustworthy, Ubiquitous Time Transfer
Secure and reliable time transfer is a key enabler for the next generation of services worldwide. A number of different applications such as 5G mobile broadband, mobile multimedia broadcast, power grids, terrestrial positioning services, financial operations, IoT, big data and cloud processing will require accurate, secure and reliable time information to be able to work consistently and…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
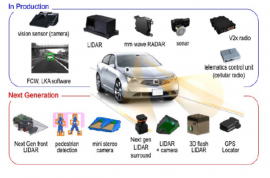
Low-Cost GNSS Antenna Arrays for Improved Performance, Anti-Spoofing, and Meaconing and Interference Mitigation
The activity primarily targets GNSS antennas for autonomous driving vehicles, which is a fast growing market.
It is foreseen that future vehicles will rely less and less on humans, and more and more on Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), requiring reliable navigation based on several sensors (GNSS and others) in order to ensure security and safety inside and outside the vehicle in all…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
Space GNSS Receiver for In-Orbit Demonstration of PPP
The object of the activity is to design, develop and validate/verified a GNSS space receiver capable to perform on board precise orbit determination (P2OD) in real time using precise GNSS orbit and clock corrections provided either by Geostationary satellites or Galileo Commercial Service (thus allowing on board autonomy w.r.t to ground stations).
The concept is similar to what is performed on…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
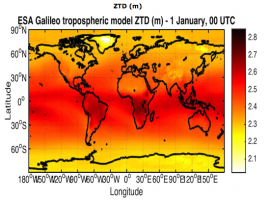
Weather Monitoring Based on Collaborative Crowdsourcing
The measurement of Integrated Water Vapour using GNSS stations from a network of reference stations have been demonstrated.
During the last years, the existence of multi- constellation and multi-frequency GNSS increases the effectiveness and reliability of such measurements for weather prediction. Currently the availability of affordable powerful hand-held GNSS receivers with…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main
Cooperative Navigation and Cloud Processing
The current evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Cities, together with the proliferation in the last years of cloud platforms where storage and processing of data can, ideally, be handled on demand, has boosted the appearance of new applications and services in the positioning domain of potential interest for specific use cases. In particular, the processing in the cloud of GNSS…
esa-STAR link: http://emits.sso.esa.int/emits/owa/emits.main